

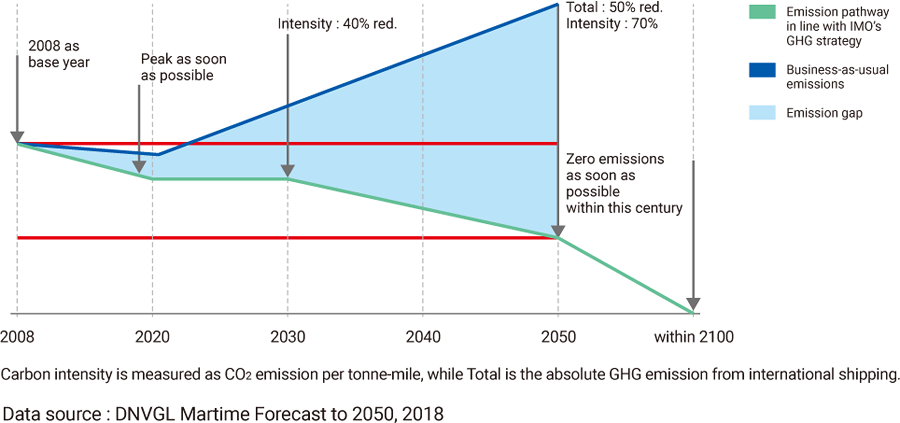
The initial IMO strategy for reduction of GHG emissions from ships are finalized and adopted.
Reduction per transport, as an average across international shipping, at least 40% by 2030, pursing effort towards 70% by 2050, as compared to 2008.
Reduce the total annual GHG emissions at least 50% by 2050 as compared to 2008.
The adoption of revised IMO strategy will be decided at the MEPC 80th meeting (Spring, 2023)
MAROL revision banning of loading HFO (higher than 0.5% Sulfur oil) on the scrubber unequipped vessel was opted.
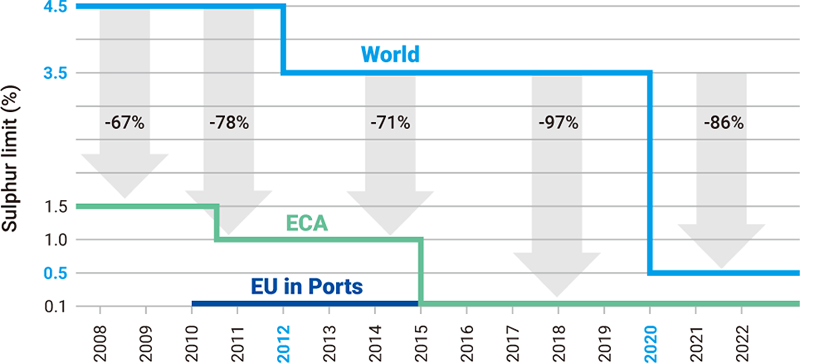
According to the sulfur cap regulation decided by the MEPC(Marine Environment Protection Committee) at October 2016, Global marine fuel’s sulfur content standard has been enhanced from 3.5% to 0.5% since January 2020.
Shipbuilding & Marine industry has to select the solutions such as Scrubber, LNG retrofit, or using low sulfur fuel oil to meet the regulation, ahead of the implementation of the most powerful global environmental regulation.
Scrubber fitted vessel is only permitted to use high sulfur fuel otherwise, it is highly prohibited to load high sulfur fuel on board. HGS has been providing customer-oriented service to meet every customers needs
by expanding business area not only supply and installation of Scrubber but also LNG retrofit and suppling low sulfur fuel from bunkering service which take over at June 2016.
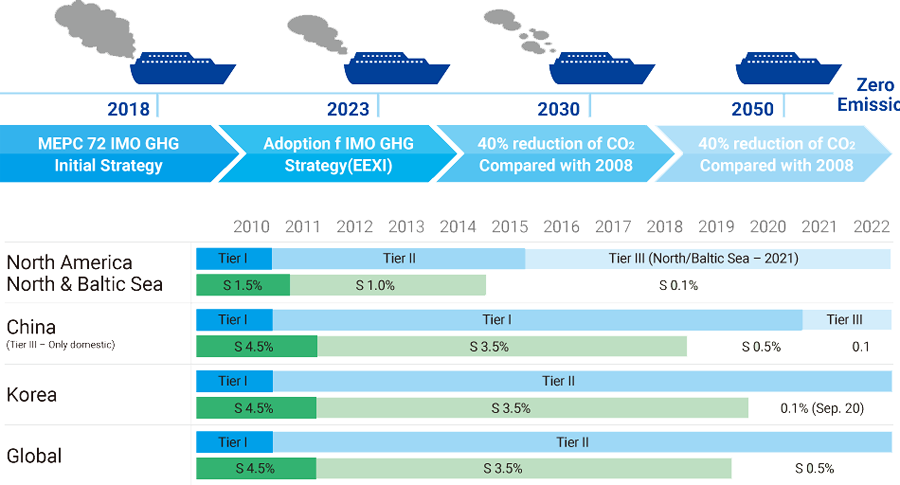
The NOx control requirements of Annex VI apply to installed marine diesel engine of over 130 kW output power other than those used solely for emergency purposes irrespective of the tonnage of the ship onto which such engines are installed. Definitions of ‘installed’ and ‘marine diesel engine’ are given in regulations 2.12 and 2.14 respectively. Different levels (Tiers) of control apply based on the ship construction date, a term defined in regulations 2.19 and hence 2.2, and within any particular Tier the actual limit value is determined from the engine’s rated speed :
| Tier | Ship construction date on or after | Total weighted cycle emission limit (g/kWh) n = engine’s rated speed (rpm) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n < 130 | n = 130 - 1999 | n ≥ 2000 | ||
| I | 1 January 2000 | 17.0 | 45·n(-0.2) e.g., 720 rpm – 12.1 |
9.8 |
| II | 1 January 2011 | 14.4 | 44·n(-0.23) e.g., 720 rpm – 9.7 |
7.7 |
| III | 1 January 2016 | 3.4 | 9·n(-0.2) e.g., 720 rpm – 2.4 |
2.0 |
| Tier | Ship construction date on or after | Total weighted cycle emission limit (g/kWh) n = engine’s rated speed (rpm) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (rpm) < 130 | 130 ≤ n < 2000 | n ≥ 2000 | ||
| I | 1 January 2000 | 17.0 | 45·n(-0.2) e.g., 720 rpm – 12.1 |
9.8 |
| II | 1 January 2011 | 14.4 | 44·n(-0.23) e.g., 720 rpm – 9.7 |
7.7 |
| III | 1 January 2016 | 3.4 | 9·n(-0.2) e.g., 720 rpm – 2.4 |
2.0 |

HMS Service Line-up v.2.2
[v.2.1] 2021-04-10Publish Website
[v.2.2] 2021-06-21Create HMS DISCOVERY Archive & Sign Up


Long Term Partnership
Eco Solution
CO₂ Emission
Fuel change
Gas Fueled Ship Package
Efficieny Optimization
Energy Saving
CO₂ Capture
Other Emission
Sea Pollution
Consulting on Regulation
Maintenance & Retrofit
Main Engine
Generator Engine
Electric System
Retrofit
Maintenance
Dry Dock
Service for Vessel
Life Cycle Risk Hedge
Qualified Supply
Asset Value Plus
Sustainable Power
Reference & Event